Residual Sum of the Squares
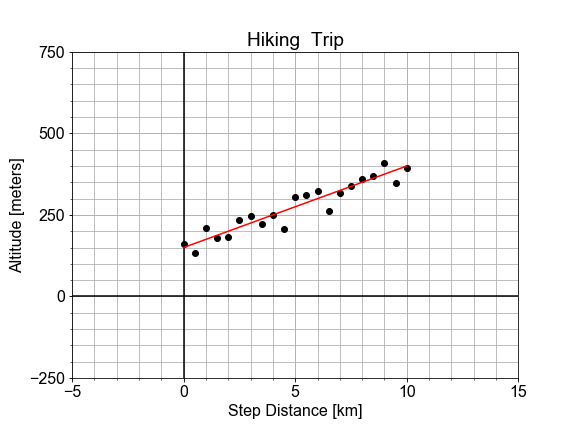
In a previous exercise, we saw that the altitude along a hiking trail was roughly fit by a linear model, and we introduced the concept of differences between the model and the data as a measure of model goodness.
In this exercise, you'll work with the same measured data, and quantifying how well a model fits it by computing the sum of the square of the "differences", also called "residuals".
This exercise is part of the course
Introduction to Linear Modeling in Python
Exercise instructions
- Load the
x_data,y_datawith the pre-definedload_data()function. - Call the pre-defined
model(), passing inx_dataand specific valuesa0,a1. - Compute the residuals as
y_data - y_modeland then findrssby usingnp.square()andnp.sum(). - Print the resulting value of
rss.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
# Load the data
x_data, y_data = load_data()
# Model the data with specified values for parameters a0, a1
y_model = model(____, a0=150, a1=25)
# Compute the RSS value for this parameterization of the model
rss = np.sum(np.square(____ - ____))
print("RSS = {}".format(____))