Linear Proportionality
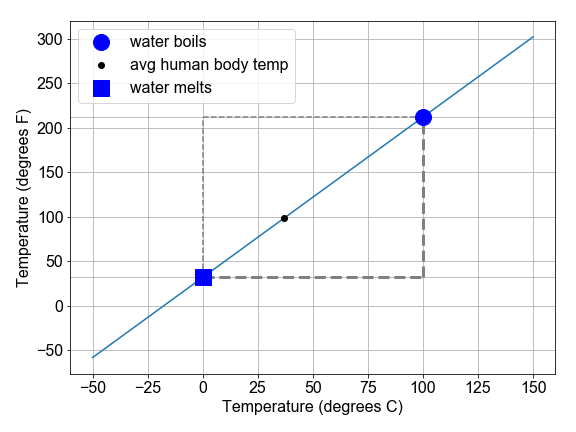
The definition of temperature scales is related to the linear expansion of certain liquids, such as mercury and alcohol. Originally, these scales were literally rulers for measuring length of fluid in the narrow marked or "graduated" tube as a proxy for temperature. The alcohol starts in a bulb, and then expands linearly into the tube, in response to increasing temperature of the bulb or whatever surrounds it.
In this exercise, we will explore the conversion between the Fahrenheit and Celsius temperature scales as a demonstration of interpreting slope and intercept of a linear relationship within a physical context.
This exercise is part of the course
Introduction to Linear Modeling in Python
Exercise instructions
- Complete the function
temps_F = convert_scale(temps_C)as a linear model where "x" istemps_Cand "y" istemps_F. - Compute the change in temperature in both scales by subtracting the freezing temperature from the boiling temperature.
- Compute the
slopeas thechange_in_Fdivided by thechange_in_C. - Compute the
interceptas the difference between the freezing pointsfreeze_Fandfreeze_C. - Use the predefined
plot_temperatures()to plot the resulting model.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
# Complete the function to convert C to F
def convert_scale(temps_C):
(freeze_C, boil_C) = (0, 100)
(freeze_F, boil_F) = (32, 212)
change_in_C = ____ - freeze_C
change_in_F = ____ - freeze_F
slope = ____ / ____
intercept = ____ - freeze_C
temps_F = ____ + (____ * temps_C)
return temps_F
# Use the convert function to compute values of F and plot them
temps_C = np.linspace(0, 100, 101)
temps_F = convert_scale(temps_C)
fig = plot_temperatures(temps_C, temps_F)