Estimation of Population Parameters
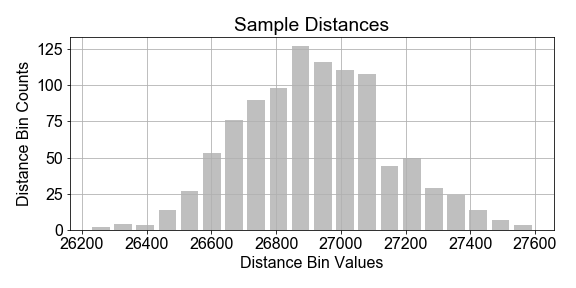
Imagine a constellation ("population") of satellites orbiting for a full year, and the distance traveled in each hour is measured in kilometers. There is variation in the distances measured from hour-to-hour, due to unknown complications of orbital dynamics. Assume we cannot measure all the data for the year, but we wish to build a population model for the variations in orbital distance per hour (speed) based on a sample of measurements.
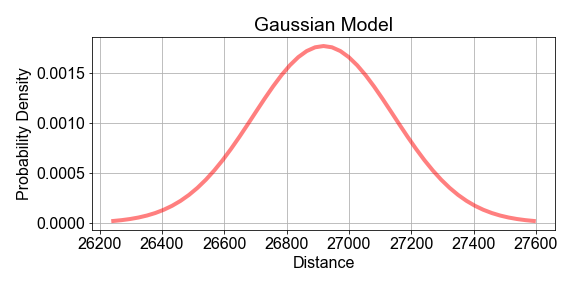
In this exercise, you will assume that the population of hourly distances are best modeled by a gaussian, and further assume that the parameters of that population model can be estimated from the sample statistics. Start with the preloaded sample_distances that was taken from a population of satellites.
This exercise is part of the course
Introduction to Linear Modeling in Python
Exercise instructions
- Compute the mean and standard deviation of the
sample_distances. - Use the sample statistics,
meanandstdev, good estimates for parametersmuandsigmaof a population model. - Pass those values, and
sample_distances, into the predefinedgaussian_model()to build the population model. - Use the predefined
plot_model_and_data()to plot the sample data and the population model together.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
# Compute the mean and standard deviation of the sample_distances
sample_mean = np.mean(____)
sample_stdev = np.std(____)
# Use the sample mean and stdev as estimates of the population model parameters mu and sigma
population_model = gaussian_model(____, mu=____, sigma=____)
# Plot the model and data to see how they compare
fig = plot_data_and_model(sample_distances, population_model)