Binomial distribution
In the previous exercise, you've modeled the Bernoulli trials. The binomial distribution is the sum of the number of successful outcomes in a set of Bernoulli trials.
The notation of the binomial distribution is \(B(n, p)\), where \(n\) is the number of experiments, and \(p\) is the probability of a success.
For this exercise, consider 10 consecutive fair coin flips. You've bet for tails and consider this outcome of a coin flip as a success.
Recall that:
dbinom(x = k, size = n, prob = p)calculates \(P(X = k)\) for \(X \sim B(n, p)\),pbinom(q = k, size = n, prob = p)calculates \(P(X \le k)\) for \(X \sim B(n, p)\).
Remember that for discrete distributions that take on whole numbers: \(P(X \ge k) = 1 - P(X \le k-1)\).
For example:
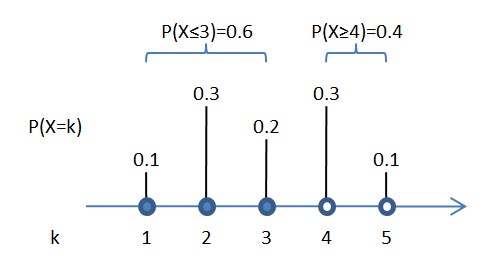
So, \(P(X \ge 4) = 1 - P(X \le 3)\).
Deze oefening maakt deel uit van de cursus
Practicing Statistics Interview Questions in R
Oefeninstructies
- Assign the probability of getting exactly 6 tails to
six_tailsand print the result. - Assign the probability of getting 7 or less tails to
seven_or_lessand print the result. - Assign the probability of getting 5 or more tails to
five_or_moreand print the result.
Praktische interactieve oefening
Probeer deze oefening eens door deze voorbeeldcode in te vullen.
# The probability of getting 6 tails
six_tails <- ___(___ = ___, size = ___, prob = ___)
print(six_tails)
# The probability of getting 7 or less tails
seven_or_less <- ___(___ = ___, size = ___, prob = ___)
print(seven_or_less)
# The probability of getting 5 or more tails
five_or_more <- 1 - ___(___ = ___, size = ___, prob = ___)
print(five_or_more)