Smoothing
Smoothing can improve the signal-to-noise ratio of your image by blurring out small variations in intensity. The Gaussian filter is excellent for this: it is a circular (or spherical) smoothing kernel that weights nearby pixels higher than distant ones.
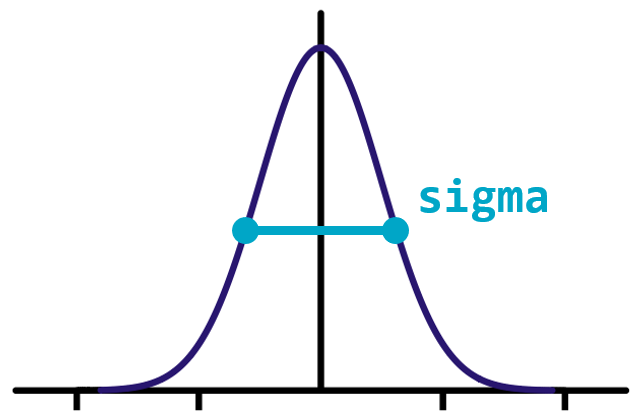
The width of the distribution is controlled by the sigma argument, with higher values leading to larger smoothing effects.
For this exercise, test the effects of applying Gaussian filters to the foot x-ray before creating a bone mask.
Cet exercice fait partie du cours
Biomedical Image Analysis in Python
Instructions
- Convolve
imwith Gaussian filters of sizesigma=1andsigma=3. - Plot the "bone masks" of
im,im_s1, andim_s3(i.e., where intensities are greater than or equal to145).
Exercice interactif pratique
Essayez cet exercice en complétant cet exemple de code.
# Smooth "im" with Gaussian filters
im_s1 = ndi.gaussian_filter(____, sigma=____)
im_s3 = ____
# Draw bone masks of each image
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1,3)
axes[0].imshow(____ >= 145)
axes[1].imshow(____)
____
format_and_render_plot()