Recherche d'un sommet de graphe à l'aide de BFS
Dans cet exercice, vous modifierez l'algorithme BFS pour rechercher un sommet donné dans un graphe.
Pour vous aider à tester votre code, le graphique suivant a été chargé à l'aide d'un dictionnaire.
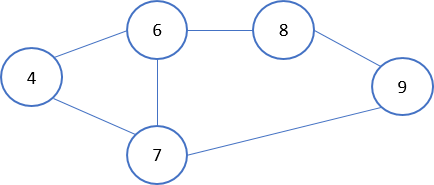
graph = {
'4' : ['6','7'],
'6' : ['4', '7', '8'],
'7' : ['4', '6', '9'],
'8' : ['6', '9'],
'9' : ['7', '8']
}
Cet exercice fait partie du cours
Structures de données et algorithmes en Python
Instructions
- Vérifiez si vous avez trouvé la valeur recherchée.
- Retournez
Truesi vous avez trouvé la valeur recherchée. - Dans la boucle
for, vérifiez si le sommet adjacent a été visité. - Retournez
Falsesi vous n'avez pas trouvé la valeur recherchée.
Exercice interactif pratique
Essayez cet exercice en complétant cet exemple de code.
import queue
def bfs(graph, initial_vertex, search_value):
visited_vertices = []
bfs_queue = queue.SimpleQueue()
visited_vertices.append(initial_vertex)
bfs_queue.put(initial_vertex)
while not bfs_queue.empty():
current_vertex = bfs_queue.get()
# Check if you found the search value
if ____:
# Return True if you find the search value
____
for adjacent_vertex in graph[current_vertex]:
# Check if the adjacent vertex has been visited
if adjacent_vertex not in ____:
visited_vertices.append(adjacent_vertex)
bfs_queue.put(adjacent_vertex)
# Return False if you didn't find the search value
____
print(bfs(graph, '4', '8'))