Coding how weight changes affect accuracy
Now you'll get to change weights in a real network and see how they affect model accuracy!
Have a look at the following neural network:
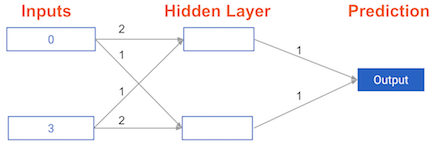
Its weights have been pre-loaded as weights_0. Your task in this exercise is to update a single weight in weights_0 to create weights_1, which gives a perfect prediction (in which the predicted value is equal to target_actual: 3).
Use a pen and paper if necessary to experiment with different combinations. You'll use the predict_with_network() function, which takes an array of data as the first argument, and weights as the second argument.
Questo esercizio fa parte del corso
Introduction to Deep Learning in Python
Istruzioni dell'esercizio
- Create a dictionary of weights called
weights_1where you have changed 1 weight fromweights_0(You only need to make 1 edit toweights_0to generate the perfect prediction). - Obtain predictions with the new weights using the
predict_with_network()function withinput_dataandweights_1. - Calculate the error for the new weights by subtracting
target_actualfrommodel_output_1. - Hit 'Submit Answer' to see how the errors compare!
Esercizio pratico interattivo
Prova a risolvere questo esercizio completando il codice di esempio.
# The data point you will make a prediction for
input_data = np.array([0, 3])
# Sample weights
weights_0 = {'node_0': [2, 1],
'node_1': [1, 2],
'output': [1, 1]
}
# The actual target value, used to calculate the error
target_actual = 3
# Make prediction using original weights
model_output_0 = predict_with_network(input_data, weights_0)
# Calculate error: error_0
error_0 = model_output_0 - target_actual
# Create weights that cause the network to make perfect prediction (3): weights_1
weights_1 = {'node_0': [____, ____],
'node_1': [____, ____],
'output': [____, ____]
}
# Make prediction using new weights: model_output_1
model_output_1 = ____
# Calculate error: error_1
error_1 = ____ - ____
# Print error_0 and error_1
print(error_0)
print(error_1)