Using pre-order traversal with Polish notation
Expression trees are a kind of binary tree that represent arithmetic expressions:
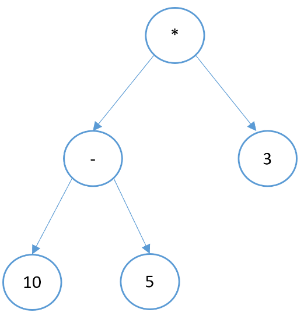
By applying in-order traversal to an expression tree, you can obtain the infix notation. This notation for the given tree will be (10-5)*3.
By applying pre-order traversal to an expression tree, you can obtain the prefix notation, aka Polish notation, where the operator appears before its operands. This notation for the given tree will be *-10 5 3.
By applying post-order traversal to an expression tree, you can obtain the postfix notation, aka reverse Polish notation, where the operator appears after its operands. This notation for the given tree will be 10 5- 3*.
Code the pre-order traversal so that you can obtain the prefix notation of this expression tree.
This exercise is part of the course
Data Structures and Algorithms in Python
Exercise instructions
- Check if
current_nodeexists. - Print the value of the
current_node. - Call the
pre_order()function recursively on the appropriate halves of the tree.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
import queue
class ExpressionTree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def pre_order(self, current_node):
# Check if current_node exists
____:
# Print the value of the current_node
____
# Call pre_order recursively on the appropriate half of the tree
____
____
et = CreateExpressionTree()
et.pre_order(et.root)