Inserting a node into a binary search tree
In the video, you learned what binary search trees (BSTs) are and how to implement their main operations.
In this exercise, you will implement a function to insert a node into a BST.
To test your code, you can use the following tree:
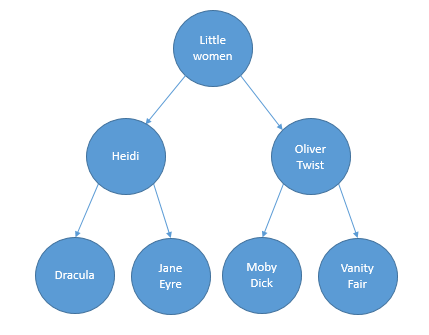
The nodes contain titles of books, building a BST based on alphabetical order.
This tree has been preloaded in the bst variable:
bst = CreateTree()
You can check if the node is correctly inserted with this code:
bst.insert("Pride and Prejudice")
print(search(bst, "Pride and Prejudice"))
This exercise is part of the course
Data Structures and Algorithms in Python
Exercise instructions
- Check if the BST is empty.
- Check if the data to insert is smaller than the current node's data.
- Check if the data to insert is greater than the current node's data.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
class BinarySearchTree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, data):
new_node = TreeNode(data)
# Check if the BST is empty
if ____ == None:
self.root = new_node
return
else:
current_node = self.root
while True:
# Check if the data to insert is smaller than the current node's data
if ____ < ____:
if current_node.left_child == None:
current_node.left_child = new_node
return
else:
current_node = current_node.left_child
# Check if the data to insert is greater than the current node's data
elif ____ > ____:
if current_node.right_child == None:
current_node.right_child = new_node
return
else:
current_node = current_node.right_child
bst = CreateTree()
bst.insert("Pride and Prejudice")
print(search(bst, "Pride and Prejudice"))