Finding a graph vertex using BFS
In this exercise, you will modify the BFS algorithm to search for a given vertex within a graph.
To help you test your code, the following graph has been loaded using a dictionary.
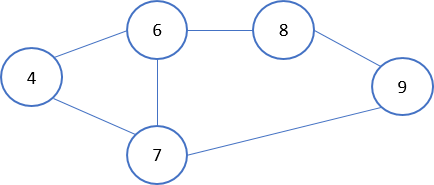
graph = {
'4' : ['6','7'],
'6' : ['4', '7', '8'],
'7' : ['4', '6', '9'],
'8' : ['6', '9'],
'9' : ['7', '8']
}
This exercise is part of the course
Data Structures and Algorithms in Python
Exercise instructions
- Check if you found the search value.
- Return
Trueif you found the search value. - Inside the
forloop, check if the adjacent vertex has been visited. - Return
Falseif you didn't find the search value.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
import queue
def bfs(graph, initial_vertex, search_value):
visited_vertices = []
bfs_queue = queue.SimpleQueue()
visited_vertices.append(initial_vertex)
bfs_queue.put(initial_vertex)
while not bfs_queue.empty():
current_vertex = bfs_queue.get()
# Check if you found the search value
if ____:
# Return True if you find the search value
____
for adjacent_vertex in graph[current_vertex]:
# Check if the adjacent vertex has been visited
if adjacent_vertex not in ____:
visited_vertices.append(adjacent_vertex)
bfs_queue.put(adjacent_vertex)
# Return False if you didn't find the search value
____
print(bfs(graph, '4', '8'))