Implementing DFS for graphs
In this exercise, you will implement a depth first search algorithm to traverse a graph.
Recall the steps:
- Start at any vertex
- Add the vertex to the visited vertices list
- For each current node's adjacent vertex
- If it has been visited -> ignore it
- If it hasn't been visited -> recursively perform DFS
To help you test your code, the following graph has been loaded using a dictionary.
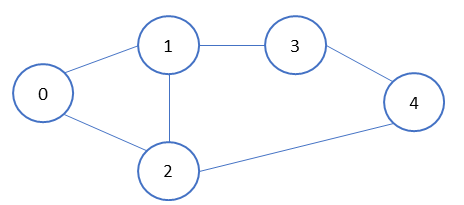
graph = {
'0' : ['1','2'],
'1' : ['0', '2', '3'],
'2' : ['0', '1', '4'],
'3' : ['1', '4'],
'4' : ['2', '3']
}
This exercise is part of the course
Data Structures and Algorithms in Python
Exercise instructions
- Check if
current_vertexhasn't been visited yet. - Add
current_vertextovisited_vertices. - Call
dfs()recursively by passing it the appropriate values.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
def dfs(visited_vertices, graph, current_vertex):
# Check if current_vertex hasn't been visited yet
if current_vertex not in ____:
print(current_vertex)
# Add current_vertex to visited_vertices
____.add(____)
for adjacent_vertex in graph[current_vertex]:
# Call recursively with the appropriate values
____(____, ____, ____)
dfs(set(), graph, '0')