Manufacturing Optimization: Search & Stop
Let's use the wall-clock factory model created in a previous exercise and deploy a "Search & Stop" optimization approach based on Monte Carlo sampling to identify the critical bottlenecks processes.
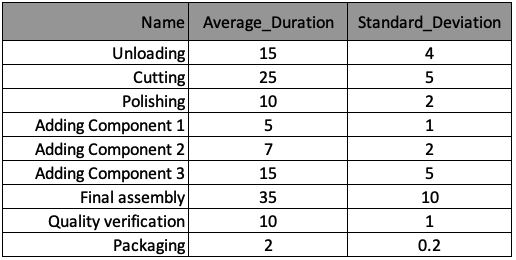
The manufacturing process is summarized in the table below, and the information has been stored in a list of dictionaries named processes, with one dictionary per process. The keys of this dictionary correspond to the table column headers.
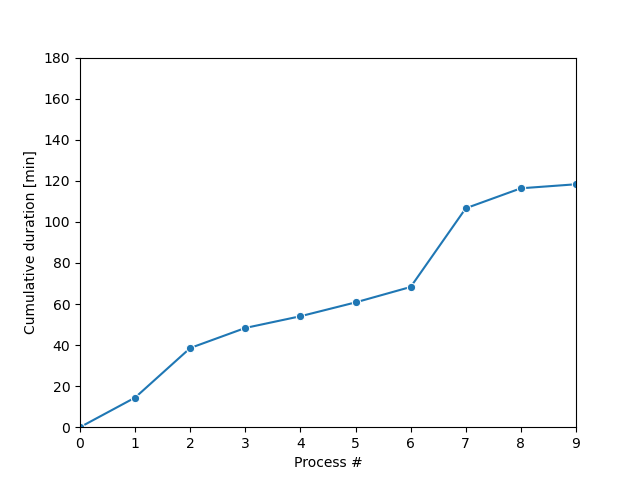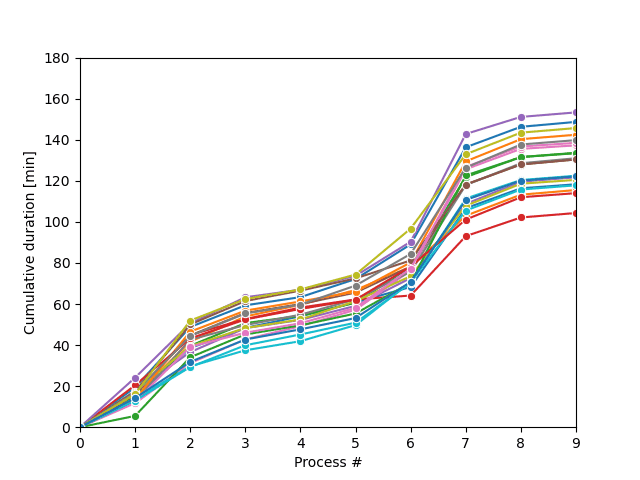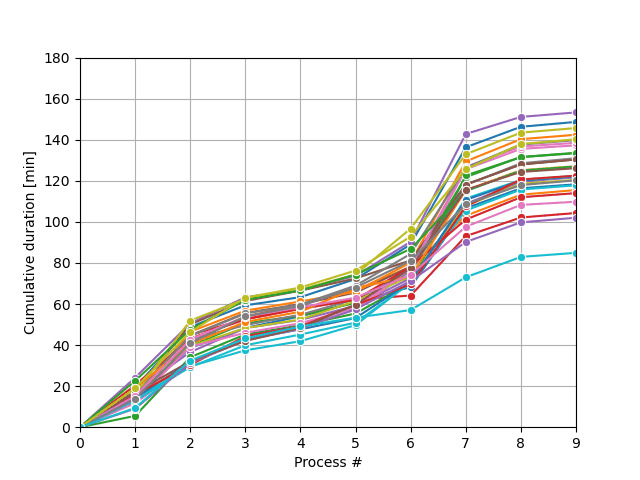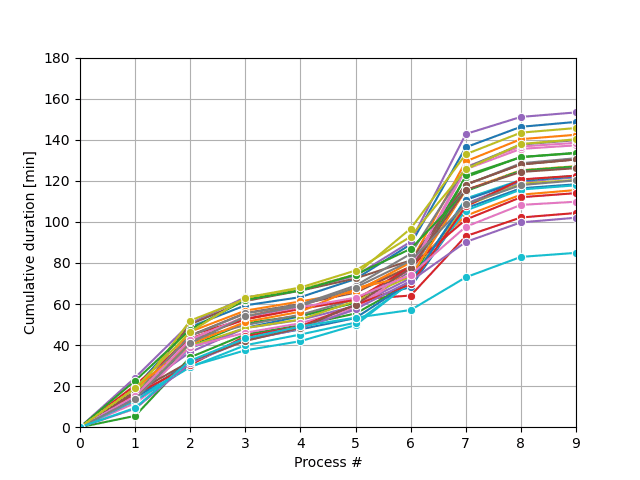
The plot_results() method to generate the plots in this exercise has been pre-loaded and is shown below.
def plot_results():
df_disc = pd.DataFrame({cNam[0]: process_line_space, cNam[1]: time_record})
fig = sns.lineplot(data=df_disc, x=cNam[0], y=cNam[1], marker='o')
plt.grid()
fig.set(xlim=(0, len(processes)))
fig.set(ylim=(0, 180))
fig.set(xticks=process_line_space)
plt.plot()
The Monte-Carlo sampling loop will produce a series of possible process trajectories and stop when the desired condition has been met, as shown in the figure.
Bu egzersiz
Discrete Event Simulation in Python
kursunun bir parçasıdırEgzersiz talimatları
- Set a loop to run simulation trajectories while
run_iis equal to zero ortotal_duration[run_i]is higher than 85 hours (i.e., stop condition:total_duration[run_i]equal or less than 85 hours). - Run the Monte Carlo engine stored in the function
run_monte_carlo().
Uygulamalı interaktif egzersiz
Bu örnek kodu tamamlayarak bu egzersizi bitirin.
def run_monte_carlo():
run_i = 0
# While-loop with the stop condition
____
run_i += 1
env = simpy.Environment()
env.process(manufractoring_process(env))
env.run()
plot_results()
plt.show()
# Call the run_monte_carlo function
____