Stack images
Image "stacks" are a useful metaphor for understanding multi-dimensional data. Each higher dimension is a stack of lower dimensional arrays.
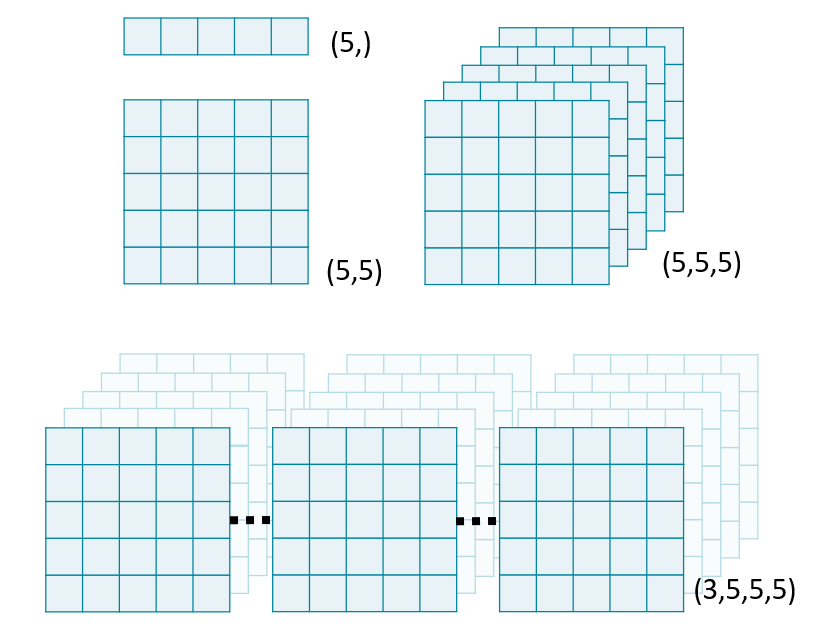
In this exercise, we will use NumPy's stack() function to combine several 2D arrays into a 3D volume. By convention, volumetric data should be stacked along the first dimension: vol[plane, row, col].
Note: performing any operations on an ImageIO Image object will convert it to a numpy.ndarray, stripping its metadata.
This exercise is part of the course
Biomedical Image Analysis in Python
Exercise instructions
- Import
imageioandnumpy(asnp). - Load "chest-220.dcm", "chest-221.dcm", and "chest-222.dcm".
- Create a 3D volume using
np.stack(). Set the stackingaxisto 0. - Print the
shapeattribute ofvol.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
# Import ImageIO and NumPy
____
import ____ as ____
# Read in each 2D image
im1 = imageio.imread('chest-220.dcm')
im2 = ____
im3 = ____
# Stack images into a volume
vol = np.stack(____)
print('Volume dimensions:', ____)