Put some Spark in your data
In the last exercise, you saw how to move data from Spark to pandas. However, maybe you want to go the other direction, and put a pandas DataFrame into a Spark cluster! The SparkSession class has a method for this as well.
The .createDataFrame() method takes a pandas DataFrame and returns a Spark DataFrame.
The output of this method is stored locally, not in the SparkSession catalog. This means that you can use all the Spark DataFrame methods on it, but you can't access the data in other contexts.
For example, a SQL query (using the .sql() method) that references your DataFrame will throw an error. To access the data in this way, you have to save it as a temporary table.
You can do this using the .createTempView() Spark DataFrame method, which takes as its only argument the name of the temporary table you'd like to register. This method registers the DataFrame as a table in the catalog, but as this table is temporary, it can only be accessed from the specific SparkSession used to create the Spark DataFrame.
There is also the method .createOrReplaceTempView(). This safely creates a new temporary table if nothing was there before, or updates an existing table if one was already defined. You'll use this method to avoid running into problems with duplicate tables.
Check out the diagram to see all the different ways your Spark data structures interact with each other.
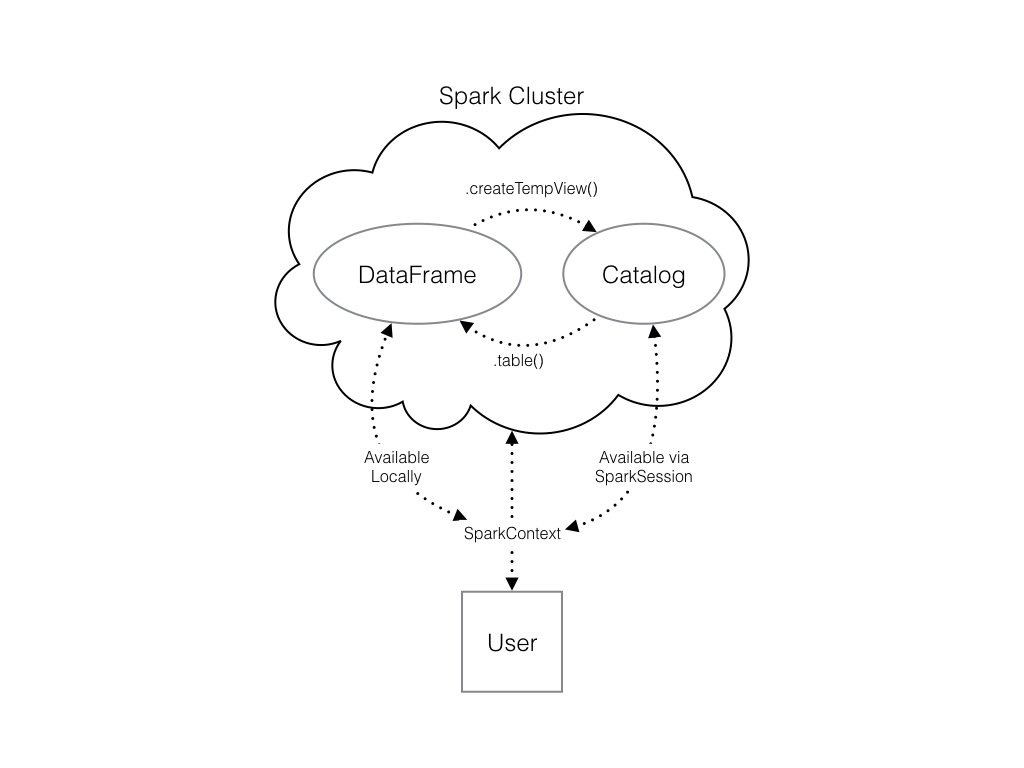
There's already a SparkSession called spark in your workspace, numpy has been imported as np, and pandas as pd.
This exercise is part of the course
Foundations of PySpark
Exercise instructions
- The code to create a
pandasDataFrame of random numbers has already been provided and saved underpd_temp. - Create a Spark DataFrame called
spark_tempby calling the Spark method.createDataFrame()withpd_tempas the argument. - Examine the list of tables in your Spark cluster and verify that the new DataFrame is not present. Remember you can use
spark.catalog.listTables()to do so. - Register the
spark_tempDataFrame you just created as a temporary table using the.createOrReplaceTempView()method. THe temporary table should be named"temp". Remember that the table name is set including it as the only argument to your method! - Examine the list of tables again.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
# Create pd_temp
pd_temp = pd.DataFrame(np.random.random(10))
# Create spark_temp from pd_temp
spark_temp = ____
# Examine the tables in the catalog
print(____)
# Add spark_temp to the catalog
spark_temp.____
# Examine the tables in the catalog again
print(____)