Uniform distribution
Questions related to the continuous uniform distribution come up during interviews because the calculations associated with this distribution are relatively straightforward.
A random variable is usually denoted as \(X\) and a continuous uniform distribution on a range \([a, b]\) is denoted as \(U(a, b)\).
Recall that punif(q = k, min = a, max = b) calculates \(P(X \le k)\) for \(X \sim U(a, b)\).
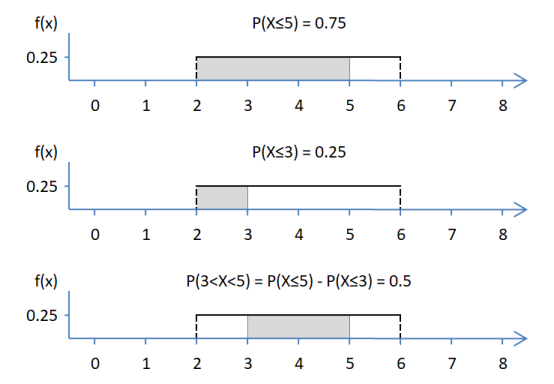
You can derive the probability that a random variable falls into a range as a difference of the two cumulative probabilities: \(P(j < X < k) = P(X \le k) - P(X \le j)\)
See the example below for \(X \sim U(2, 6)\):
This exercise is part of the course
Practicing Statistics Interview Questions in R
Hands-on interactive exercise
Turn theory into action with one of our interactive exercises
 Start Exercise
Start Exercise