Wrong input distributions
You'll continue working with the pi example in this exercise:
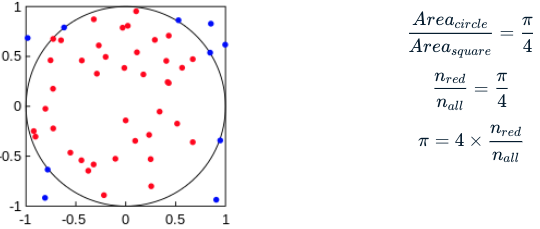
What happens if you change the input probability distribution from the continuous uniform distribution(random.uniform()) to the discrete uniform distribution(random.randint())? Your results will not be reliable, because random.randint() will sample discrete integers, while random.uniform() samples continuous float numbers.
Pay attention to the estimated pi value that this simulation generates. Because the incorrect probability distribution has been selected, it will not be very accurate! Choosing the correct probability distributions is essential for Monte Carlo simulations, and we will go into more detail on different distributions in later lessons so that you feel confident you are choosing the correct one going forward.
random has been imported for you.
This exercise is part of the course
Monte Carlo Simulations in Python
Exercise instructions
- Sample the
xandycoordinates in the interval from -1 to 1 usingrandom.randint()rather than the correctrandom.uniform()function used in the video.
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
n = 10000
circle_points = 0
square_points = 0
for i in range(n):
# Sample the x and y coordinates from -1 to 1 using random.randint()
x = ____
y = ____
dist_from_origin = x**2 + y**2
if dist_from_origin <= 1:
circle_points += 1
square_points += 1
pi = 4 * circle_points / square_points
print(pi)