The linear algebra of dense layers
There are two ways to define a dense layer in tensorflow. The first involves the use of low-level, linear algebraic operations. The second makes use of high-level keras operations. In this exercise, we will use the first method to construct the network shown in the image below.
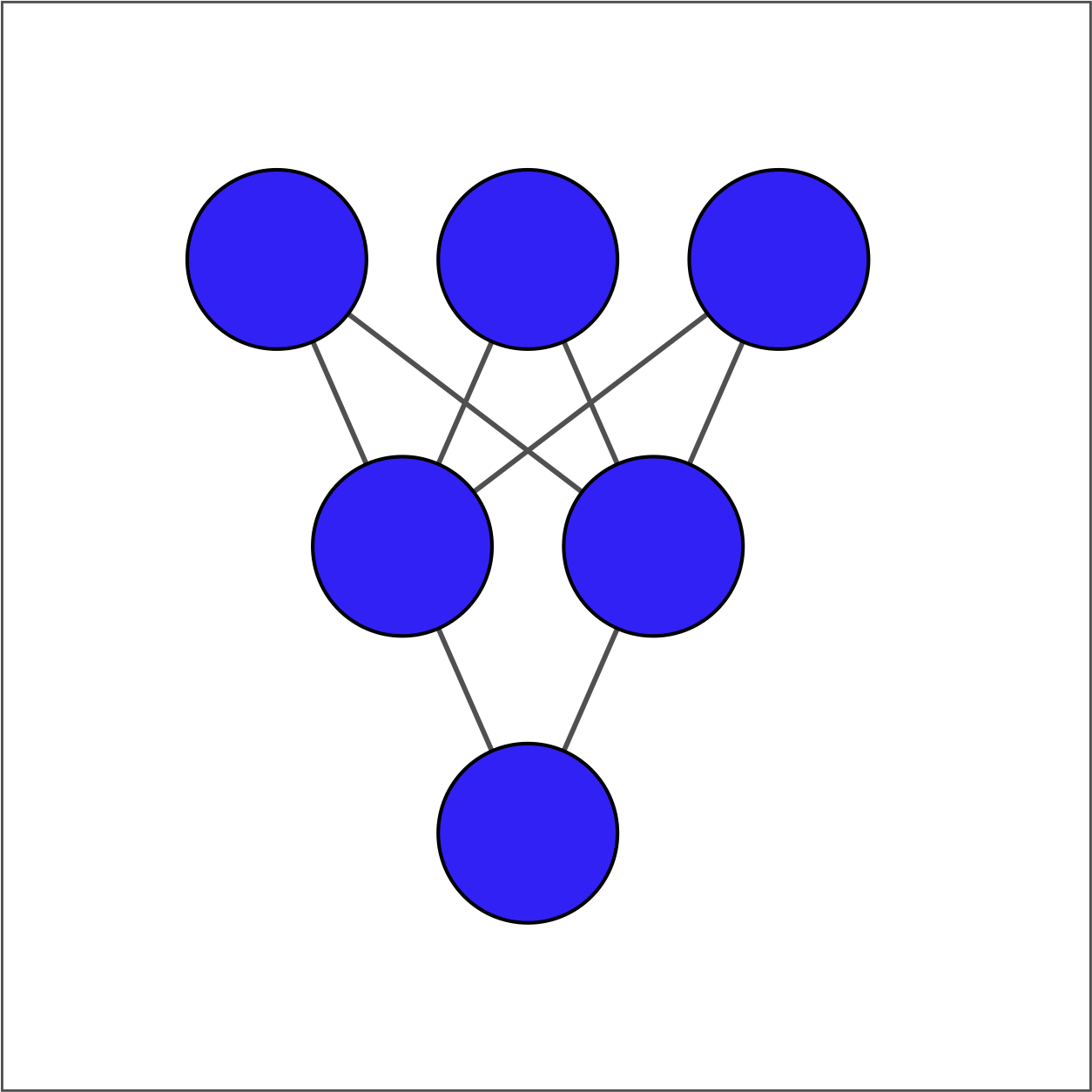
The input layer contains 3 features -- education, marital status, and age -- which are available as borrower_features. The hidden layer contains 2 nodes and the output layer contains a single node.
For each layer, you will take the previous layer as an input, initialize a set of weights, compute the product of the inputs and weights, and then apply an activation function. Note that Variable(), ones(), matmul(), and keras() have been imported from tensorflow.
This exercise is part of the course
Introduction to TensorFlow in Python
Hands-on interactive exercise
Have a go at this exercise by completing this sample code.
# Initialize bias1
bias1 = Variable(1.0)
# Initialize weights1 as 3x2 variable of ones
weights1 = ____(ones((____, ____)))
# Perform matrix multiplication of borrower_features and weights1
product1 = ____
# Apply sigmoid activation function to product1 + bias1
dense1 = keras.activations.____(____ + ____)
# Print shape of dense1
print("\n dense1's output shape: {}".format(dense1.shape))